Topotek Gimbals¶
Topotek provides a wide variety of camera gimbals which communicate with ArduPilot using a custom serial protocol. The smallest is the GIP335 which weighs 60g

Warning
Support for these gimbals is available in ArduPilot 4.6 (and higher)
Where to Buy¶
These gimbals can be purchased directly from Topotek
Connecting to the Autopilot¶
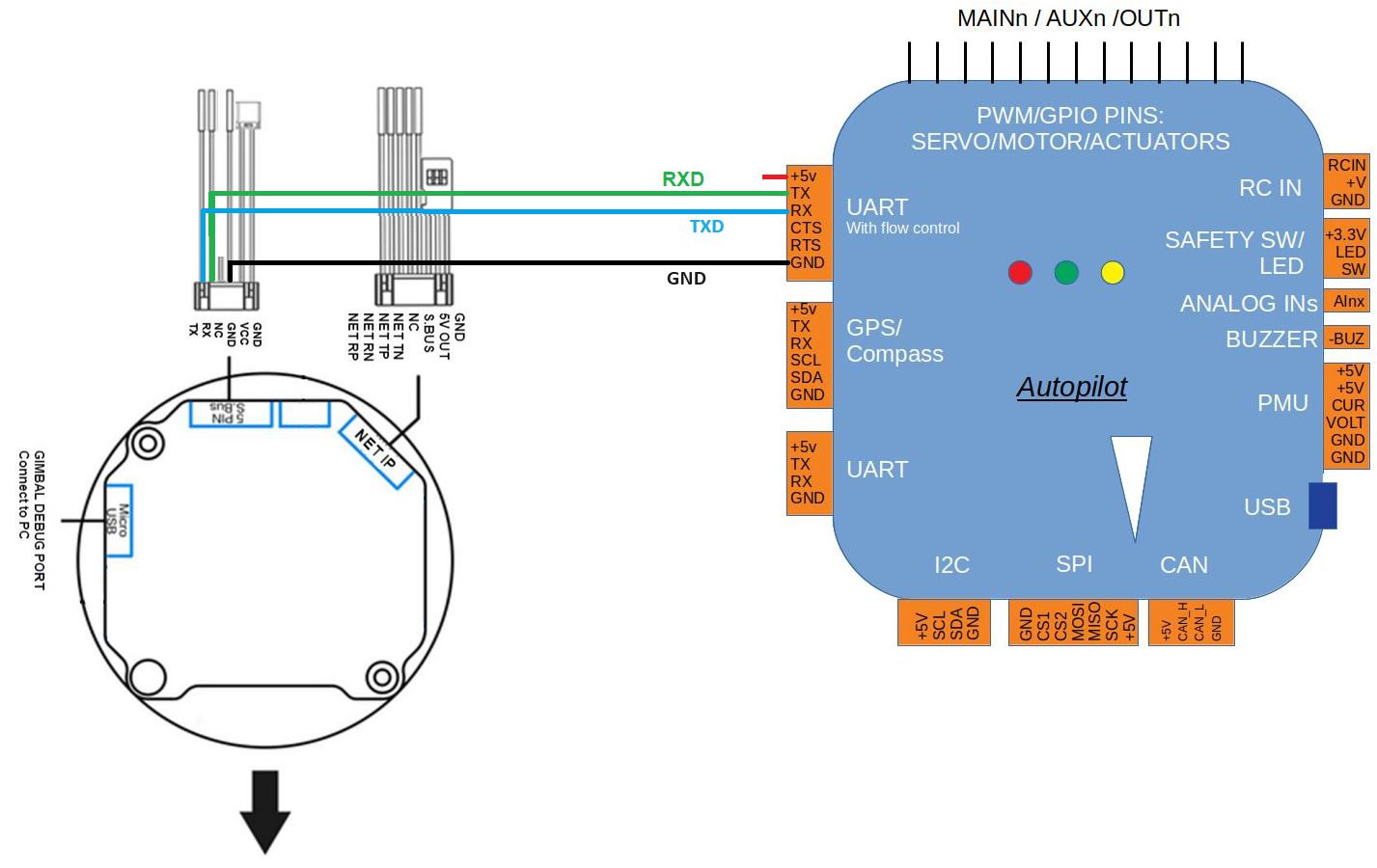
Connect the gimbal’s RX, TX and GND pins to one of the autopilot’s serial ports as shown above.
Connect with a ground station and set the following parameters. The params below assume the autopilot’s telem2 port is used and the Camera1 control instance,
SERIAL2_PROTOCOL to 8 (“Gimbal”)
SERIAL2_BAUD to “115” for 115200 bps
MNT1_TYPE to “12” (“Topotek”) and reboot the autopilot
MNT1_PITCH_MIN to -90
MNT1_PITCH_MAX to 45
MNT1_YAW_MIN to -180
MNT1_YAW_MAX to 180
MNT1_RC_RATE to 60 (deg/s) to control speed of gimbal when using RC targeting
CAM1_TYPE to 4 / “Mount” to allow control of the camera
RC6_OPTION = 213 (“Mount Pitch”) to control the gimbal’s pitch angle with RC channel 6
RC7_OPTION = 214 (“Mount Yaw”) to control the gimbal’s yaw angle with RC channel 7
RC8_OPTION = 163 (“Mount Lock”) to switch between “lock” and “follow” mode with RC channel 8
Optionally these auxiliary functions are also available
RC9_OPTION = 9 (“Camera Trigger”) to take a picture
RC9_OPTION = 166 (“Camera Record Video”) to start/stop recording of video
RC9_OPTION = 167 (“Camera Zoom”) to zoom in and out
RC9_OPTION = 168 (“Camera Manual Focus”) to adjust focus in and out
RC9_OPTION = 169 (“Camera Auto Focus”) to trigger auto focus
Configuring the Gimbal¶
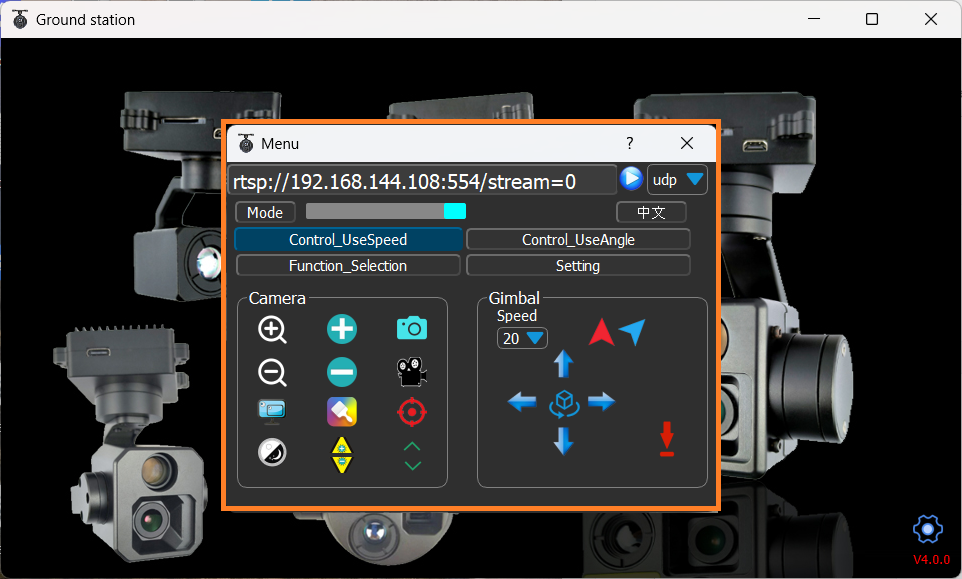
The camera gimbal can be configured over an Ethernet connection using the “GimbalControl” application which can be downloaded from the Topotek Download Resources page
To configure using the serial port use the “Angle control” or “Speed control” applications which can also be downloaded from Topotek Download Resources page
Ethernet Connectivity¶
Instead of using a UART serial connection, an Ethernet connection may be used to both control the gimbal and display live video stream from the camera
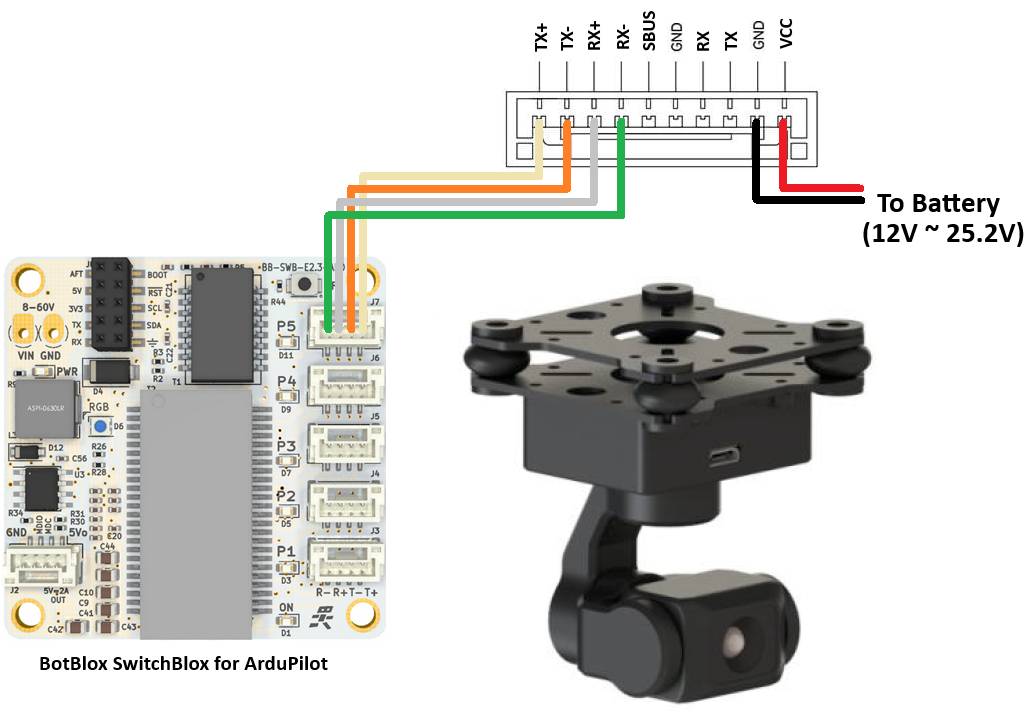
An example setup of a networked ArduPilot vehicle system is detailed in Ethernet Connected Vehicle Example
Connect the gimbal and autopilot using an ethernet adapter
Ensure the autopilot and gimbal are on the same subnet (e.g the first 3 octets of the IP address match, 4th octet is different)
The gimbal’s IP address can be set using the “GimbalControl” application (see image above)
Set the autopilot’s NET_ENABLE = 1 and reboot to enable networking
Set the autopilot’s IP address using NET_IPADDR0, NET_IPADDR1, NET_IPADDR2, NET_IPADDR3 (e.g. 192.168.144.14)
Create a serial connection over ethernet
Set NET_P1_TYPE = 1 (UDP Client) and reboot the autopilot
Set NET_P1_IP0, NET_P1_IP1, NET_P1_IP2, NET_P1_IP3 to the gimbal’s IP address (e.g. 192.168.144.108)
Set NET_P1_PORT = 9003 (port that gimbal listens for commands on)
Set NET_P1_PROTOCOL = 8 (Gimbal)
Two video streams are available on different RTSP URLs
“rtsp://192.168.144.108:554/stream=0” provides a 1080p stream
“rtsp://192.168.144.108:554/stream=1” provides a 480p stream
If connected to a PC, VLC can be used to test the feed
Set the PC’s IP address so the first three octets match the camera’s IP address which, by default, is 192.168.144.108
Open VLC
Select “Media”, “Open Network Stream” and enter one of the RTSP URLS listed above
If using QGC, the live video can be configured from the “Application Settings”, “General” screen. Set “Source” to “RTSP Video Stream” and “RTSP URL” to one of the RTSP URLs listed above
If using Mission Planner, the live video can be displayed on the Data screen by following these instructions
Firmware Updates¶
At least some Topotek gimbals support upgrading the firmware via SD card
Email Topotek and request the latest firmware. The email address can be found at the bottom of the topotek.com website
Eject the gimbal’s SD card and insert it into a computer
Copy the firmware into a file folder named “topotek” in the root directory of the SD card
Replace the SD card back into the gimbal
Powerup the Gimbal and it should update within 20 seconds
Remove the SD card, delete the firmware file and reinsert the SD card into the gimbal
Downloading Images and Video¶
Images and videos captured by the camera gimbal can be remotely downloaded via Ethernet
If a Windows PC is used:
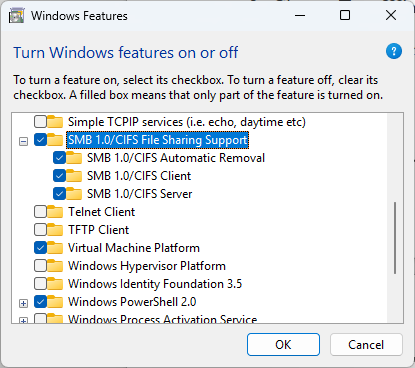
Enable SMB file sharing support (Microsoft instructions are here)
From the Start menu search for “Turn Windows Features on or off”
Enable “SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support”
Open Settings, Network & internet, Ethernet and set the PC’s IP address so the first three octets match the camera’s IP address (e.g. setting to 192.168.144.99 should work)
Open a file explorer and enter the camera’s IP address,
\\192.168.144.108, into the address barImages and videos can be found in the
camera/DCIM/snapandcamera/DCIM/recorddirectories respectively
If a Linux/Ubuntu PC is used:
Install “smbclient” and “cifs-utils” packages (e.g.
sudo apt-get install smbclient cifs-utils)Edit the “/etc/fstab” file and add an entry to the bottom like below
//192.168.144.108/camera /media/windowsshare cifs vers=1.0,guest,uid=1000 0 0
Set the PC’s IP address so the first three octets match the camera’s IP address (e.g. setting to 192.168.144.99 should work)
Mount the shared directory (e.g.
sudo mount /media/windowsshare)The images and videos can be found in the
/media/windowsshare/DCIM/snapand/media/windowsshare/DCIM/recorddirectories respectively
Control and Testing¶
See Gimbal / Mount Controls and Camera Controls for details on how to control the camera and gimbal using RC, GCS or Auto mode mission commands