DroneBridge / ESP32 WiFi telemetry¶
ESP32 are readily available Wi-Fi modules with full TCP/IP stack and microcontroller capability. They offer dedicated UART, SPI and I2C interfaces.
DroneBridge for ESP32 for the popular ESP32 modules from Espressif Systems offers a transparent and bi-directional serial to WiFi bridge. In addition it features a custom ESP-NOW implementation which allows for ranges of up to 1km. It is one of the cheapest ways to communicate with ardupilot wirelessly.
It also allows for a fully transparent serial to WiFi pass-through link with variable packet size.| DroneBridge for ESP32 is a telemetry/low data rate-only solution. There is no support for cameras connected to the ESP32 since it does not support video encoding.
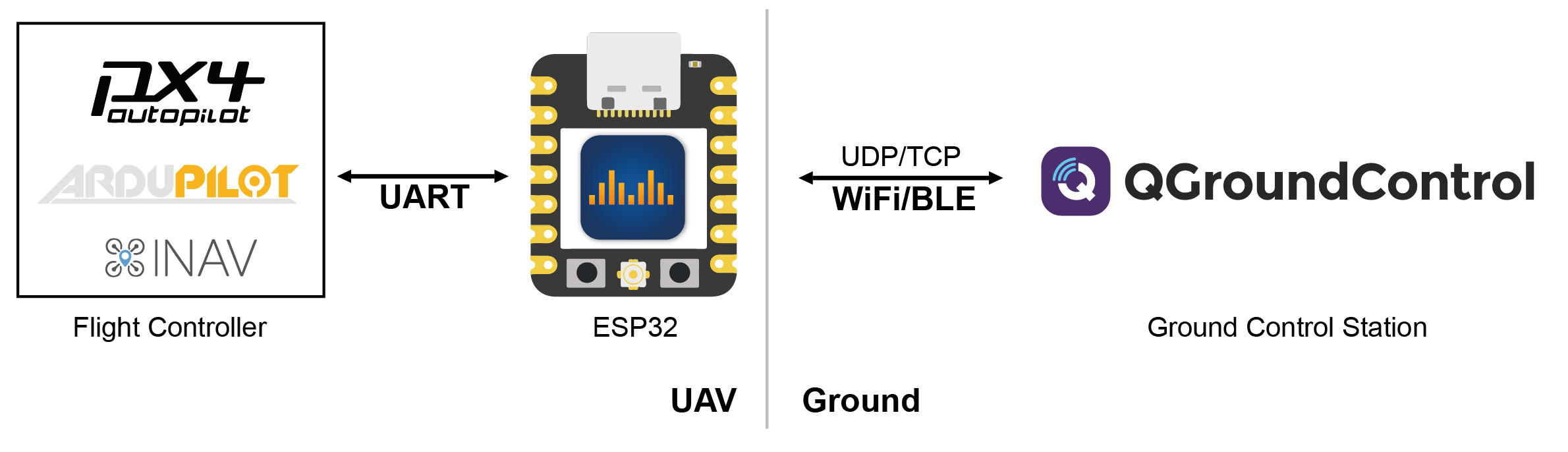
DroneBridge for ESP32 supports standard WiFi connections to an access point but can also operate as a standalone access point.
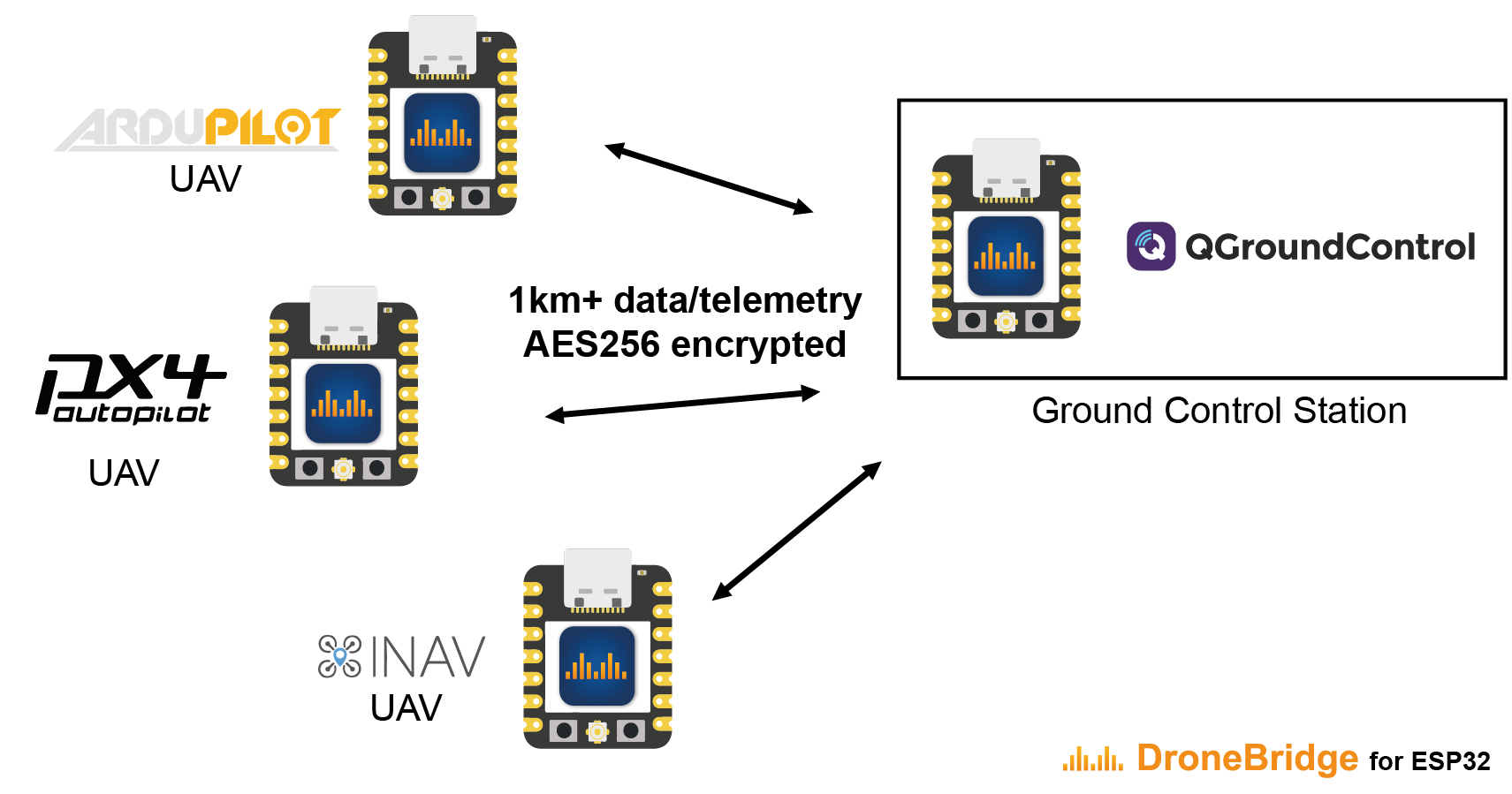
The ESP-NOW mode offers a connectionless and encrypted alternative to traditional WiFi. While the data rate is reduced to ~250 kbit/s the range is increased up to 1 km. This mode has no limit on how many clients are connected on the autopilot side. Only channel capacity and processing capacity limit the number of clients. This mode requires ESP32 devices on the GCS side as well as on the autopilot side.
Features¶
Bidirectional: serial-to-WiFi, serial-to-WiFi Long-Range (LR), serial-to-ESP-NOW link
Support for MAVLink, MSP, LTM or any other payload using transparent option
Affordable, Reliable & low latency
Weight: <8 g
Up to 150m range using standard WiFi
Up to 1km of range using ESP-NOW or Wi-Fi LR Mode - sender & receiver must be ESP32 with LR-Mode enabled
Fully encrypted in all modes including ESP-NOW broadcasts secured using AES-GCM 256 bit!
Supported by: QGroundControl, Mission Planner, mwptools, impload etc.
Easy to set up: Power connection + UART connection to flight controller
Fully configurable through an easy-to-use web interface
Parsing of LTM & MSPv2 for more reliable connection and less packet loss
Parsing of MAVLink with the injection of Radio Status packets for the display of RSSI in the GCS
Fully transparent telemetry down-link option
Support for drone swarms of almost any size using ESP-NOW with its custom & encrypted broadcast mode
Recommended Hardware¶
Every ESP32 board is capable of running DroneBridge for ESP32. Boards and modules with an external antenna connector are recommended, since those will likely offer more range.
Warning
Most modules support 3.3V input (only), while some autopilots serial ports provide 5V . You will need to check compatibility and step down the voltage if needed. It is not generally recommended to use the autopilot’s 3.3V supply unless you are certain it can provide enough current for the ESP32 board you are using.
Officially Supported and Tested Boards¶
Do the project and yourself a favour and use one of the officially supported and tested boards below. These boards are very low in price, have everything you need and are also very small. Perfect for use on any drone.
You can find all the latest information on the official boards on the website.
Downloading and Flashing the Firmware¶
An easy-to-use online flashing tool is available on the official website. Just connect your ESP32 and click flash! For more detailed information please visit the official Wiki!
Configuring DroneBridge for ESP32¶
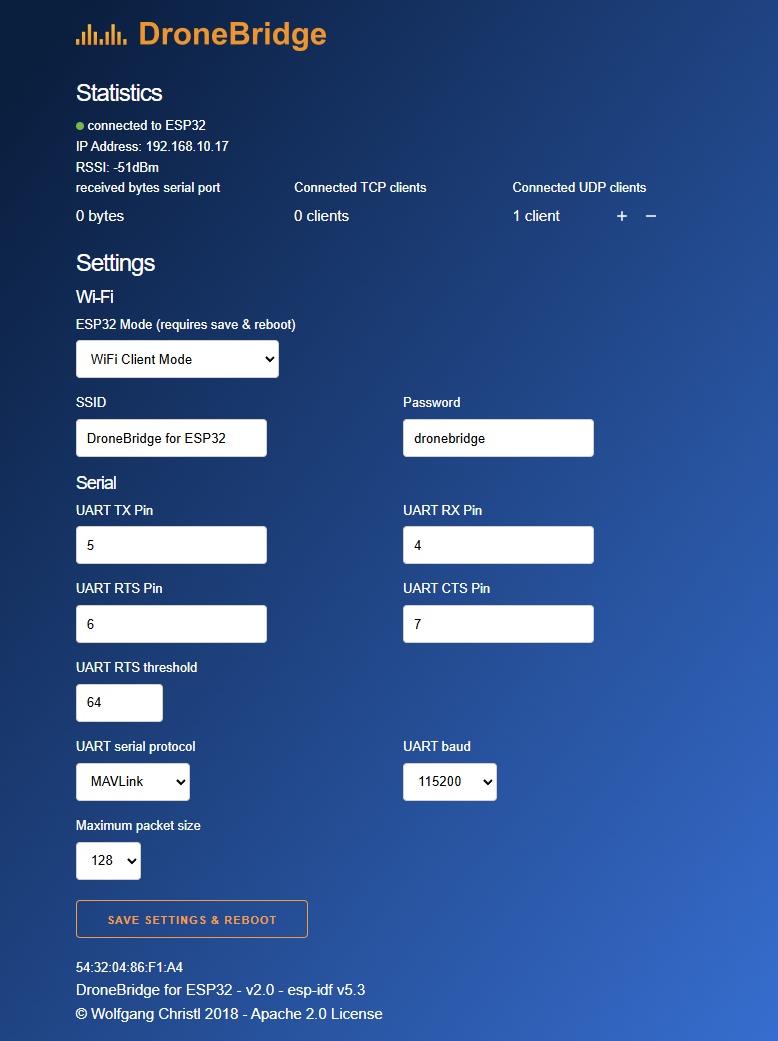
You can change the default configuration via the Web Interface.
Connect to the ESP32 via WiFi and enter dronebridge.local, http://dronebridge.local or 192.168.2.1 in the address
bar of your browser.
Wiring¶
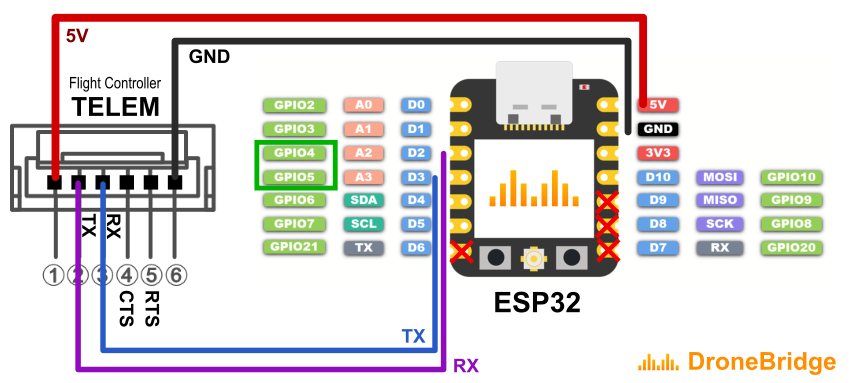
Wiring is very simple and mostly the same for all devices connected to any serial port (ie. TELEM1 or TELEM2) of the autopilot. This guide does not go into detail here but provides an outline for wiring below.
Connect UART of ESP32 to a UART of your autopilot (ie. TELEM 1 or TELEM 2 port). Make sure the voltage levels match! Most ESP32 DevKits can only take 3.3V!
TX to RX
RX to TX
GND to GND
Stable 3.3V or 5V power supply to the ESP32 (depending on the available inputs of your ESP32 and capabilities of the autopilot)
Set the autopilot port to MAVLINK 1 or 2 protocol.
Note
Some manufacturers of ESP32 DevKits have the wrong labels for the pins on their products. Make sure that the PINs on your board are labeled correctly if you encounter issues.
Make sure to always follow the instructions of the ESP32 board manufacturer when it comes to wiring. Especially the power supply.
ArduPilot configuration¶
Configure the UART of the autopilot that is wired to the ESP32 to have matching baud rates and MAVLink set as protocol for optimal performance.
for example, if connected to SERAIL2 port on the autopilot these parameters should be set:
SERIAL2_PROTOCOL = 2 (MAVLink2) or 1 (MAVLink1)
SERIAL2_BAUD = 115 (115200 baud)
If you have problems connecting, it may help to set BRD_SER2_RTSCTS = 0 to disable flow control although this is not normally necessary
Connection to the GCS¶
The following connection options are available:
UDP unicast on port
14550to all connected devices.TCP on port
5760
DroneBridge for ESP32 will automatically forward all data to all connected WiFi devices via UDP to port 14550. QGroundControl or Mission Planner should auto-detect the connection and no further actions should be necessary.
For use with Mission Planner it may be neessary to check the Config, Planner, “Disable RTS reset on ESP32 SerialUSB” checkbox as shown below
APIs,Troubleshooting & Support¶
For more detailed information please visit the official Wiki!