MAVLink Basics¶
MAVLink is a serial protocol most commonly used to send data and commands between vehicles and ground stations
The protocol defines a large set of messages which can be found in common.xml and ardupilot.xml
MAVLink messages can be sent over almost any serial connection and does not depend upon the underlying technology (wifi, 900mhz radio, etc)
The messages are not guaranteed to be delivered which means ground stations or companion computers must often check the state of the vehicle to determine if a command has been executed
Message Format¶
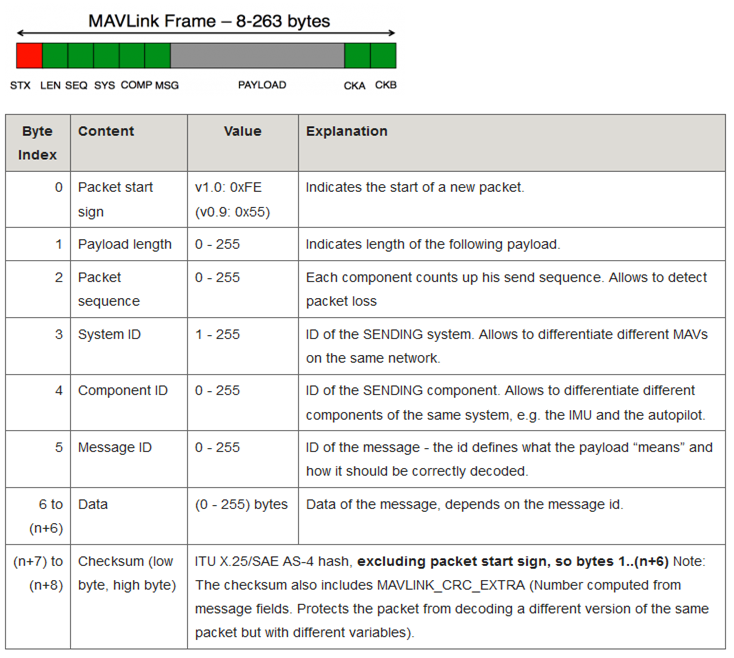
Messages are no more than 263 bytes (Mavlink version1.0) or 280 bytes (Mavlink version 2.0).
The sender always fills in the
System IDandComponent IDfields so that the receiver knows where the packet came from. TheSystem IDis a unique ID for each vehicle or ground station. Ground stations normally use a high system id like “255” and vehicles default to use “1” (this can be changed by setting the MAV_SYSID parameter, see also MAV_GCS_SYSID and MAV_GCS_SYSID_HI). TheComponent IDfor the ground station or flight controller is normally “1”. Other MAVLink capable device on the vehicle (i.e. companion computer, gimbal) should use the sameSystem IDas the flight controller but use a differentComponent IDThe
Message IDfield can be seen in the common.xml and ardupilot.xml next to the message name. For example the HEARTBEAT message Id is “0”The
Dataportion of the message holds the individual field values being sentSee this page for advice on how to add support for a new MAVLink message
High Level Message Flow¶
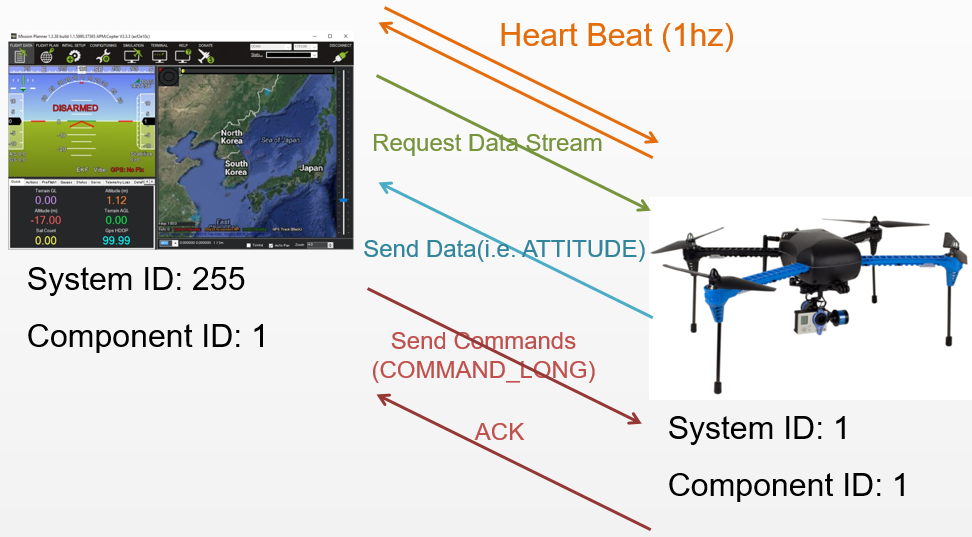
Once a connection is opened each device (aka “System”) sends the HEARTBEAT message at 1hz
The ground station or companion computer requests the data it wants (and the rate) by sending messages of the following types
REQUEST_DATA_STREAM supports setting the rate of groups of messages
COMMAND_LONG containing a SET_MESSAGE_INTERVAL command provides precise control of which messages are sent (and their rate) but is only supported on ArduPilot 4.0 and higher
Ground station or companion computer send commands to the vehicle. Details of the supported commands are here for copter and plane
MAVLink1(v1) vs MAVLink2(v2)¶
In this document, MAVLink protocol versions v1 and v2 are referred to as MAVLink1 and MAVLink2 respectively.
- MAVLink2 messages have a maximum of 280 bytes of length, as they implement compatibility flags and support for signature.
- MAVLink2 extends MAVLink1 by allowing new fields to be added to existing MAVLink1 messages, supports new messages with Message ID over “255” and adds support for signing messages
- MAVLink2 is backwards compatible with MAVLink1 meaning that if a device understands MAVLink2 messages it certainly understands MAVLink1 messages
- If a device only capable of understanding MAVLink1 receives a message that includes additional fields (added under MAVLink2) the device will only see the original fields. I.e. the device will be able to read the message but will not “see” the additional fields
- A flight controller’s serial port (presumably connected to a telemetry radio) can be set to use MAVLink2 by setting the SERIALx_PROTOCOL parameter to “2” (where “x” is the serial port number on the flight controller)
- See Mavlink2 Documentation for more information (especially on message extensions)