Adding a New Flight Mode to Copter¶
This section covers the basics of how to create a new high level flight mode (i.e. equivalent of Stabilize, Loiter, etc)
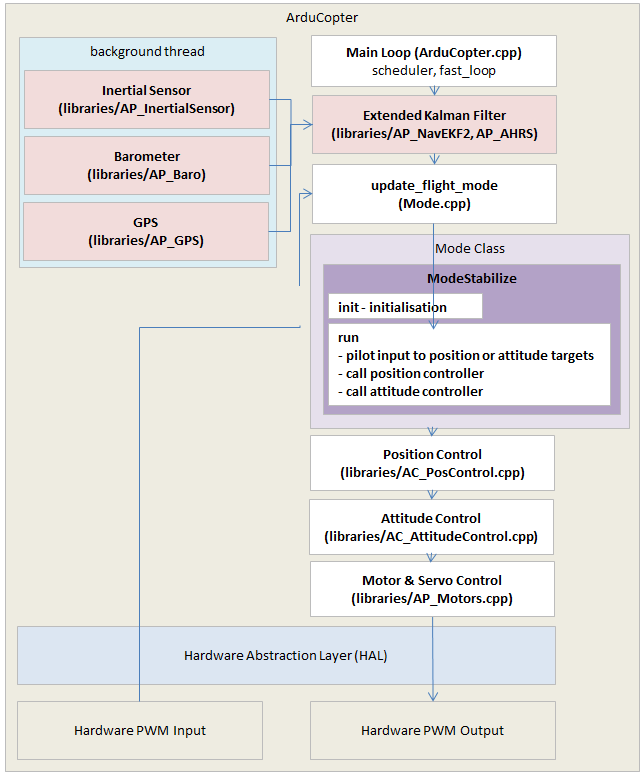
As a reference the diagram below provides a high level view of Copter’s architecture.
Pick a name for the new mode and add it to the bottom of the control_mode_t enum in mode.h just like “NEW_MODE” has been added below.
// Auto Pilot Modes enumeration enum class Number { STABILIZE = 0, // manual airframe angle with manual throttle ACRO = 1, // manual body-frame angular rate with manual throttle ALT_HOLD = 2, // manual airframe angle with automatic throttle AUTO = 3, // fully automatic waypoint control using mission commands GUIDED = 4, // fully automatic fly to coordinate or fly at velocity/direction using GCS immediate commands LOITER = 5, // automatic horizontal acceleration with automatic throttle RTL = 6, // automatic return to launching point CIRCLE = 7, // automatic circular flight with automatic throttle LAND = 9, // automatic landing with horizontal position control DRIFT = 11, // semi-automous position, yaw and throttle control SPORT = 13, // manual earth-frame angular rate control with manual throttle FLIP = 14, // automatically flip the vehicle on the roll axis AUTOTUNE = 15, // automatically tune the vehicle's roll and pitch gains POSHOLD = 16, // automatic position hold with manual override, with automatic throttle BRAKE = 17, // full-brake using inertial/GPS system, no pilot input THROW = 18, // throw to launch mode using inertial/GPS system, no pilot input AVOID_ADSB = 19, // automatic avoidance of obstacles in the macro scale - e.g. full-sized aircraft GUIDED_NOGPS = 20, // guided mode but only accepts attitude and altitude SMART_RTL = 21, // SMART_RTL returns to home by retracing its steps FLOWHOLD = 22, // FLOWHOLD holds position with optical flow without rangefinder FOLLOW = 23, // follow attempts to follow another vehicle or ground station ZIGZAG = 24, // ZIGZAG mode is able to fly in a zigzag manner with predefined point A and point B SYSTEMID = 25, // System ID mode produces automated system identification signals in the controllers AUTOROTATE = 26, // Autonomous autorotation NEW_MODE = 27, // your new flight mode };
Define a new class for the mode in mode.h. It is probably easiest to copy a similar existing mode’s class definition and just change the class name (i.e. copy and rename “class ModeStabilize” to “class ModeNewMode”). The new class should inherit from the Mode class and implement
run(),name()andname4()and optionallyinit().public: // inherit constructor using Mode::Mode; bool init(bool ignore_checks) override; void run() override; protected: const char *name() const override { return "NEWMODE"; } const char *name4() const override { return "NEWM"; }
The
name()andname4()methods are for logging and display purposes.init()will be called when the vehicle first switches into this new mode so it should implement any required initialisation.run()will be called at 400hz and should implement any pilot input decoding and then set position and attitude targets (see below).There are also some simple methods returning true/false that you may want to override that control features such as whether the vehicle can be armed in the new mode:
bool requires_GPS() const override { return false; } bool has_manual_throttle() const override { return true; } bool allows_arming(bool from_gcs) const override { return true; }; bool is_autopilot() const override { return false; }
Create a new mode_<new flight mode>.cpp file based on a similar mode such as mode_stabilize.cpp or mode_loiter.cpp. This new file should probably implement the
init()method which will be called when the vehicle first enters the mode. This function should return true if it is OK for the vehicle to enter the mode, false if it cannot. Below is an excerpt from mode_rtl.cpp’s init method that shows how the vehicle cannot enter RTL mode unless the home position has been set.// rtl_init - initialise rtl controller bool ModeRTL::init(bool ignore_checks) { if (!ignore_checks) { if (!AP::ahrs().home_is_set()) { return false; } } // initialise waypoint and spline controller wp_nav->wp_and_spline_init(); _state = RTL_Starting; _state_complete = true; // see run() method below terrain_following_allowed = !copter.failsafe.terrain; return true; }Below is an excerpt from mode_stabilize.cpp’s run method (called 400 times per second) that decodes the user’s input, then sends new targets to the attitude controller.
void ModeStabilize::run() { // convert pilot input to lean angles float target_roll, target_pitch; get_pilot_desired_lean_angles(target_roll, target_pitch, copter.aparm.angle_max, copter.aparm.angle_max); // get pilot's desired yaw rate float target_yaw_rate = get_pilot_desired_yaw_rate(channel_yaw->get_control_in()); // code that sets motor spool state omitted // call attitude controller attitude_control->input_euler_angle_roll_pitch_euler_rate_yaw(target_roll, target_pitch, target_yaw_rate); // output pilot's throttle attitude_control->set_throttle_out(get_pilot_desired_throttle(), true, g.throttle_filt);
Instantiate the new mode class in Copter.h by searching for “ModeAcro” and then adding the new mode somewhere below.
Mode *flightmode; #if MODE_ACRO_ENABLED == ENABLED #if FRAME_CONFIG == HELI_FRAME ModeAcro_Heli mode_acro; #else ModeAcro mode_acro; #endif #endif ModeAltHold mode_althold; #if MODE_AUTO_ENABLED == ENABLED ModeAuto mode_auto; #endif #if AUTOTUNE_ENABLED == ENABLED AutoTune autotune; ModeAutoTune mode_autotune; #endif
In mode.cpp add the new mode to the
mode_from_mode_num()function to create the mapping between the mode’s number and the instance of the class.// return the static controller object corresponding to supplied mode Mode *Copter::mode_from_mode_num(const Mode::Number mode) { Mode *ret = nullptr; switch (mode) { case ACRO: ret = &mode_acro; break; case STABILIZE: ret = &mode_stabilize; break;
Add the new flight mode to the list of valid
@Valuesfor theFLTMODE1 ~ FLTMODE6parameters in Parameters.cpp (Search for “FLTMODE1”). Once committed to master, this will cause the new mode to appear in the ground stations list of valid modes. Note that even before being committed to master, a user can setup the new flight mode to be activated from the transmitter’s flight mode switch by directly setting the FLTMODE1 (or FLTMODE2, etc) parameters to the number of the new mode.// @Param: FLTMODE1 // @DisplayName: Flight Mode 1 // @Description: Flight mode when Channel 5 pwm is <= 1230 // @Values: 0:Stabilize,1:Acro,2:AltHold,3:Auto,4:Guided,5:Loiter,6:RTL,7:Circle,9:Land,11:Drift,13:Sport,14:Flip,15:AutoTune,16:PosHold,17:Brake,18:Throw,19:Avoid_ADSB,20:Guided_NoGPS,21:Smart_RTL,22:FlowHold,23:Follow,24:ZigZag // @User: Standard GSCALAR(flight_mode1, "FLTMODE1", FLIGHT_MODE_1), // @Param: FLTMODE2 // @DisplayName: Flight Mode 2 // @Description: Flight mode when Channel 5 pwm is >1230, <= 1360 // @Values: 0:Stabilize,1:Acro,2:AltHold,3:Auto,4:Guided,5:Loiter,6:RTL,7:Circle,9:Land,11:Drift,13:Sport,14:Flip,15:AutoTune,16:PosHold,17:Brake,18:Throw,19:Avoid_ADSB,20:Guided_NoGPS,21:Smart_RTL,22:FlowHold,23:Follow,24:ZigZag // @User: Standard GSCALAR(flight_mode2, "FLTMODE2", FLIGHT_MODE_2),
Optionally you may wish to add the flight mode to the
COPTER_MODEenum within the mavlink/ardupilotmega.xml because some ground stations may use this to automatically populate the list of available flight modes.